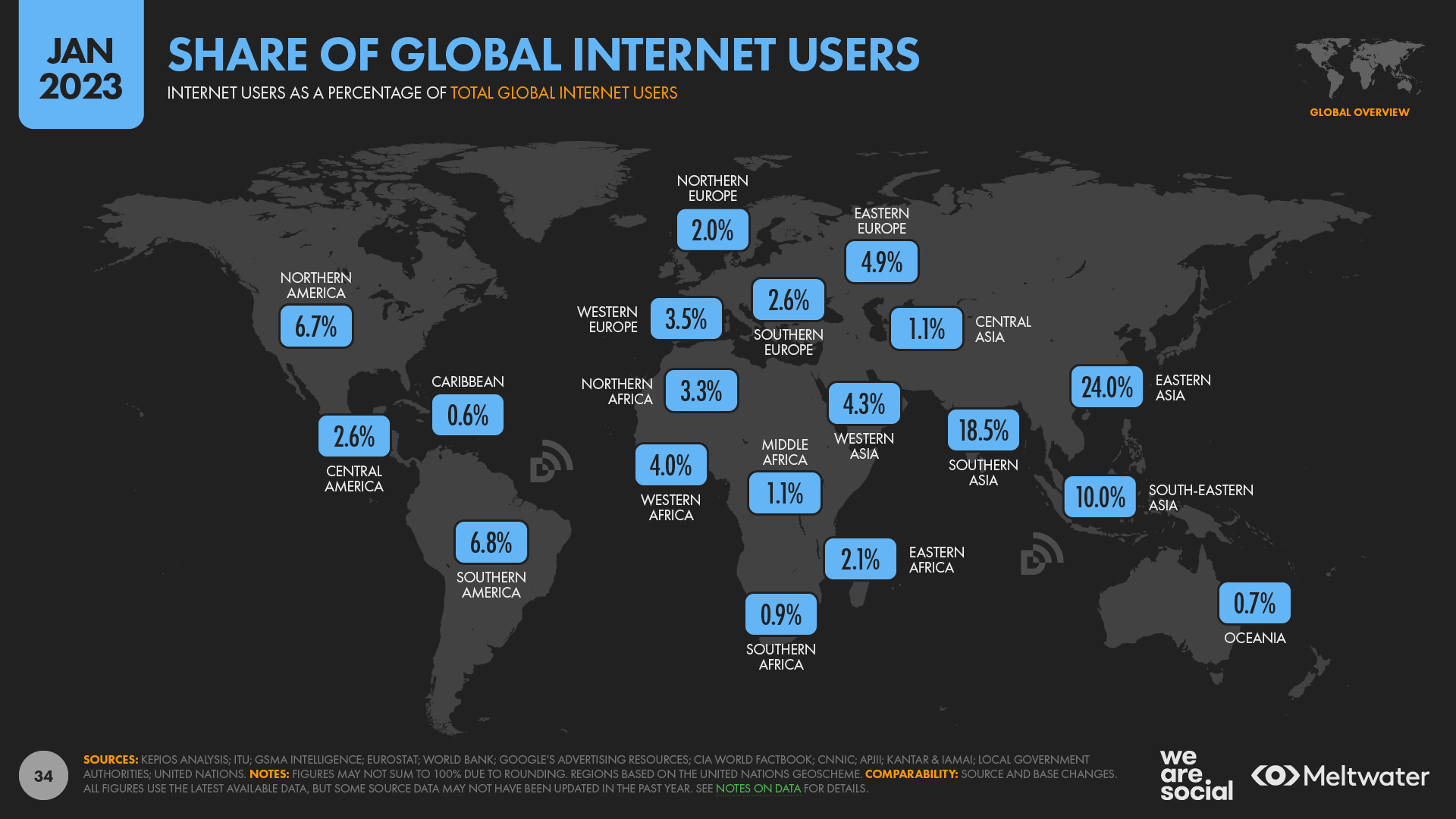
The terrain of global internet access presents a complex tableau marked by both progress and stark inequalities. While approximately 60% of the world's population is now online, regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia continue to face considerable challenges, with connectivity rates plummeting to as low as 29.3%. This disparity is further complicated by socioeconomic factors and demographic differences, which raise critical questions about the future of digital inclusion. As mobile networks emerge as a crucial solution, one must consider the consequences for infrastructure investment and digital literacy initiatives moving forward.
Global Internet User Overview
As of 2023, approximately 60% of the global population, translating to over 4.7 billion individuals, possesses internet access, marking a significant milestone in digital connectivity.
Despite this progress, internet accessibility challenges persist, particularly in underrepresented regions such as Africa and South America. The digital divide remains a pressing issue, with socioeconomic factors contributing to disparities in access.
Solutions to bridge this gap include infrastructure investment, government policies promoting digital literacy, and community-based initiatives aimed at increasing connectivity.
Addressing these challenges is essential to guarantee that all individuals can benefit from the opportunities that the internet offers, nurturing empowerment and freedom in an increasingly digital world.
Regional Access Disparities
While internet access has made notable strides globally, substantial disparities persist across different regions, highlighting a complex interplay of socioeconomic and geographical factors. In regions like North America, the internet usage rate reaches 91%, contrasted sharply with Sub-Saharan Africa's mere 29.3%. Accessibility initiatives are vital in addressing these gaps, as improved internet literacy can enable communities to utilize available resources effectively.
| Region | Internet Access Rate |
|---|---|
| North America | 91% |
| Europe | 86.5% |
| South Asia | 38.5% |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 29.3% |
These figures underscore the urgent need for targeted interventions to improve connectivity and advocate for equitable access to information in underrepresented areas.
Demographic Variations in Access
Demographic variations in internet access reveal notable disparities influenced by factors such as age, gender, location, and socioeconomic status.
For instance, while 94% of non-disabled households enjoy internet connectivity, only 76% of households with disabilities can access the web.
Additionally, cultural barriers greatly impact access; only 6% of Afghan women are online, reflecting ingrained societal norms.
Younger populations generally exhibit higher digital literacy and internet usage, contrasting sharply with older demographics, where only 88% of those aged 65 and older are online.
Geographic disparities persist, with urban areas benefiting from improved infrastructure compared to rural counterparts.
Addressing these demographic gaps is vital for promoting inclusivity and ensuring equitable access to the digital world, enabling all individuals to participate fully in society.
Internet Usage in the U.S
Internet usage in the United States reflects a high level of connectivity that varies across age groups and demographic factors. Approximately 96% of U.S. adults are online, with nearly universal access among children aged 3-18.
However, disparities persist, particularly among older adults, where only 88% engage with the internet. Social media platforms play a vital role in shaping digital interactions, yet users frequently express privacy concerns regarding data security and personal information.
Urban households exhibit higher connectivity rates compared to their rural counterparts, highlighting the necessity of infrastructure investment.
As internet access continues to evolve, addressing privacy issues and bridging demographic gaps will be essential in ensuring equitable access and enabling all citizens in the digital age.
Trends Among Teen Internet Users
A substantial portion of teenagers in the United States actively engages with the internet, reflecting distinct usage patterns shaped by various factors. Importantly, 46% of teens report near-constant internet use, with notable differences in platforms; 91% of teen boys favor gaming consoles, while 95% of teen girls prefer computers and 97% utilize smartphones.
These trends illustrate diverse teen online behavior influenced by social dynamics and parental guidance, as 99% of affluent, educated parents provide internet access.
Additionally, the rise in digital safety awareness among teens cannot be overlooked, as they navigate potential online risks. This heightened consciousness is vital for encouraging responsible internet use, thereby equipping adolescents to thrive in an increasingly digital environment while safeguarding their personal information.
Mobile Access and Smartphone Usage
With the rapid expansion of mobile networks, access to the internet via smartphones has become increasingly prevalent across various demographics.
The smartphone evolution has greatly influenced global connectivity, with 99.9% of internet users in China relying on mobile internet for online access. Globally, there are 5.65 billion unique mobile phone users, and 87% of these devices are internet-enabled.
This shift highlights the decreasing reliance on desktop computers, as evidenced by the 15% of U.S. adults who access the internet solely through smartphones.
Mobile internet solutions have also expanded access in rural areas, enhancing communication and information dissemination.
As smartphone technology continues to advance, its role in bridging the digital divide remains critical for promoting freedom and opportunity in the digital age.
Economic Influences on Connectivity
Economic development serves as an essential determinant of internet connectivity, greatly influencing access rates across different regions. In economies where growth is robust, there tends to be a notable correlation with higher internet penetration and usage. This relationship highlights the importance of connectivity investment, which is fundamental for nurturing a vibrant digital economy.
Infrastructure development, including broadband expansion and affordable internet services, directly impacts access levels. In addition, regions with substantial investment in technology and education experience improved connectivity, driving participation in the global digital environment.
Conversely, areas lacking such investment often see stark disparities, limiting access to key resources and opportunities. Addressing these economic influences is critical for achieving equitable connectivity and enabling communities worldwide.
Mobile Network Expansion Impact
Investment in mobile network infrastructure has emerged as a key driver for enhancing internet access, particularly in underserved regions. The expansion of mobile networks considerably improves rural connectivity, bridging gaps where traditional broadband solutions are insufficient.
With over 5.65 billion unique mobile phone users globally, affordable internet access becomes increasingly attainable through these networks. This growth nurtures an inclusive tech community that enables individuals with essential resources for education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
As mobile internet solutions proliferate, the cost of internet-enabled devices decreases, further democratizing access. Ultimately, the strategic investment in mobile networks is not only a catalyst for connectivity but also a cornerstone for promoting socio-economic development and encouraging freedom through access to information.
Challenges in High-Income Countries
Despite the high levels of internet penetration in high-income countries, considerable challenges persist that hinder universal connectivity. While 93% of populations are online, growth rates lag below 1% annually, indicating stagnation.
Digital adoption barriers, such as socioeconomic disparities and varying levels of technological literacy, contribute to this issue. Certain demographics exhibit internet access resistance, often due to cultural attitudes and a lack of perceived necessity. For instance, older adults show markedly lower engagement rates, with only 88% of those aged 65 and older accessing the internet.
To achieve thorough connectivity, addressing these barriers is essential. Continued efforts must focus on promoting inclusive digital environments that encourage participation from all societal segments, ensuring that freedom of access becomes a reality for everyone.
Future of Global Internet Access
As high-income countries grapple with stagnating internet growth rates, the future of global internet access presents both challenges and opportunities for expansion.
The pressing need for digital equity remains crucial, as billions are still offline, particularly in low-income regions. Initiatives focused on improving infrastructure will be essential for nurturing internet sustainability, enabling connectivity that is both affordable and reliable.
Innovative technologies, such as satellite internet and mobile networks, promise to reach underserved populations, thereby narrowing the digital divide.
Moreover, collaboration among governments, private sectors, and NGOs can guarantee that internet access evolves into a universal right.
The ongoing commitment to equitable access will ultimately strengthen individuals and communities, facilitating greater participation in the global digital economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Has COVID-19 Affected Global Internet Access Trends?
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated remote work and online education adoption, highlighting the digital divide. Increased reliance on telehealth services and e-commerce growth underscored the necessity for equitable internet access as an essential pandemic response strategy.
What Role Do Government Policies Play in Internet Accessibility?
Government policies greatly shape internet accessibility through regulatory frameworks that either bridge or widen the digital divide. Effective legislation encourages infrastructure investment and equitable access, while inadequate policies may perpetuate disparities in connectivity among different demographics.
How Does Internet Access Impact Education in Low-Income Regions?
Internet access considerably improves education in low-income regions by boosting digital literacy and providing access to online resources. This connectivity cultivates learning opportunities, enabling students to engage with educational content vital for academic and professional development.
Are There Initiatives Aimed at Improving Internet Access for Disabled Individuals?
Initiatives aimed at improving internet access for disabled individuals often focus on assistive technology and promoting digital inclusion. These efforts boost connectivity, ensuring equitable access to information and resources essential for participation in society.
What Technological Advancements Are Driving Future Internet Connectivity Growth?
"Necessity is the mother of invention." Future internet connectivity growth is driven by 5G technology, satellite internet, fiber optics, and the Internet of Things, enhancing accessibility and supporting an increasingly interconnected global society.